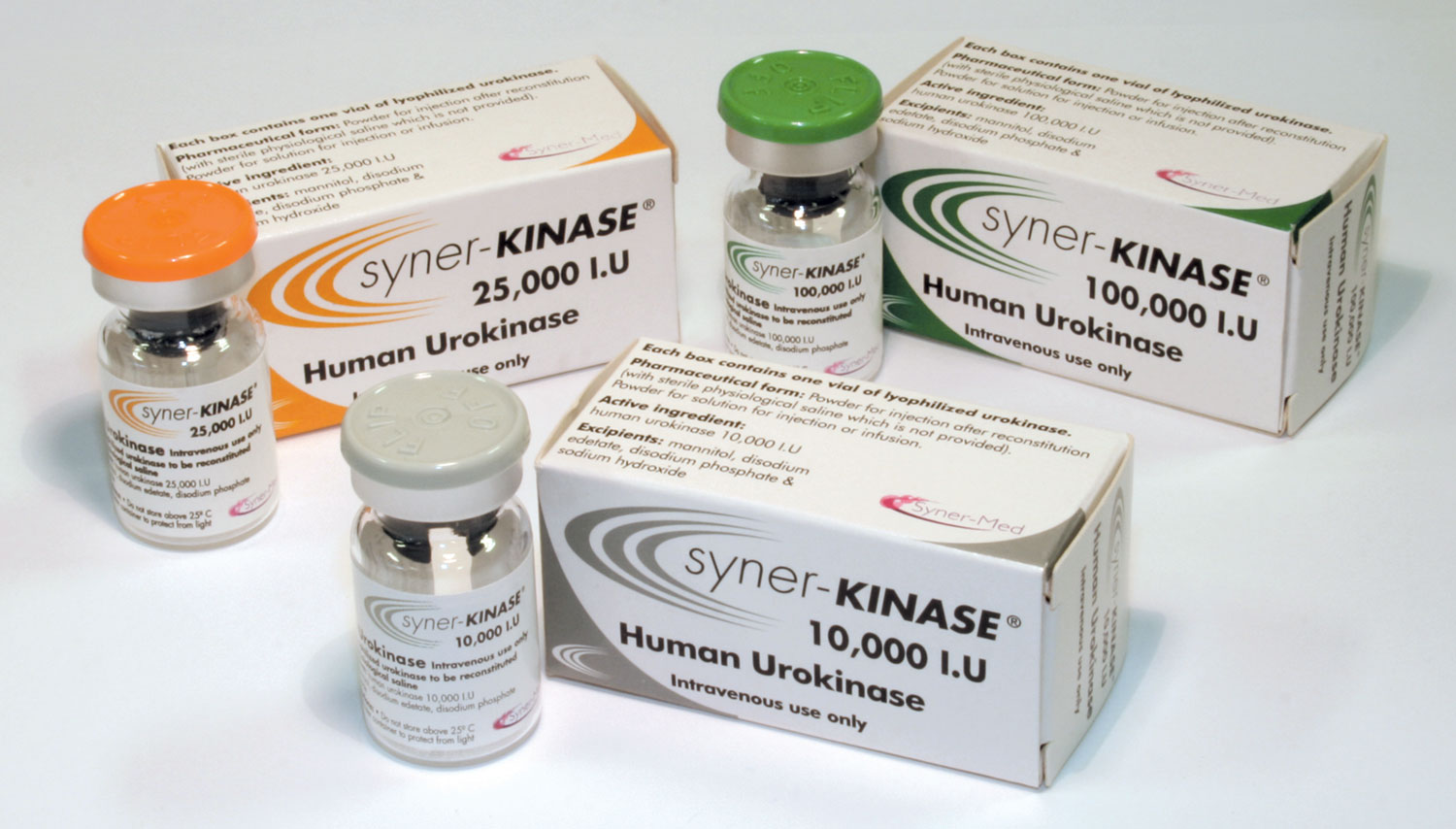
An effective algorithm for occluded catheter treatment using urokinase
An effective algorithm for occluded catheter treatment using urokinase
Managing catheter occlusions effectively is vital in clinical environments, as maintaining catheter patency is necessary to avoid treatment interruptions. The current multidisciplinary approach to catheter management combines clinical examination, imaging studies and targeted thrombolytic therapy to address catheter dysfunctions. Syner-KINASE® (urokinase) – a human urokinase protein and plasminogen activator – is a clinically proven thrombolytic agent for restoring catheter function.
Syner-KINASE in action: evidence from the PASSPORT studies
The Prospective Audit to Study urokinaSe use to restore Patency in Occluded centRal venous caTheters (PASSPORT 1 and 2) studies demonstrated Syner-KINASE’s effectiveness as a clot-dissolving medication as part of a standardised, algorithm-based approach to catheter management.
Standardised approaches to catheter management
The Syner-KINASE algorithms below were developed based on evidence from the PASSPORT 1 and PASSPORT 2 studies. They provide clear, step-by-step approaches to restoring catheter function in varied clinical settings.
Achieving high catheter clearance success rates
Achieving high catheter clearance success rates
With an initial clearance rate of up to 91 % when using infusion with doses of 100,000 to 125,000 IU – and further improvements with subsequent treatments – Syner-KINASE is highly effective in restoring catheter function, and helps to reduce the need for costly and disruptive catheter replacements.1 It is a widely used and effective option among thrombolytic therapy drugs for targeting thrombotic catheter occlusions.
Urokinase and NHS guidelines
Urokinase and NHS guidelines
The British National Formulary (BNF) provides guidance on the use of urokinase, describing it as a thrombolytic agent indicated for the treatment of thrombotic occlusions, including catheter clearance. Urokinase is administered to restore catheter patency by breaking down fibrin-rich clots, helping to maintain vascular access. For recommended dosage and administration guidelines, refer to the BNF entry on urokinase.3 The use of urokinase for the treatment of thrombotic occlusions is also recommended in guidelines published by other healthcare organisations such as the UK Kidney Association.4
Discover more about Syner-KINASE
Discover more about Syner-KINASE
Adverse events should be reported. Reporting forms and information can be found at www.mhra.gov.uk/yellowcard.
Adverse events should also be reported to Syner-Med (PP) Ltd. Tel: +44 (0)208 655 6380
For Syner-KINASE prescribing information, click here
References
- Kumwenda MJ, et al. Prospective audit to study urokinase use to restore patency in occluded central venous catheters (PASSPORT 1). The Journal of Vascular Access. 2019;20(6):752-759. doi:10.1177/1129729819869095
- Kumwenda MJ, et al. Prospective audit to study urokinase use to restore patency in occluded central venous catheters in haematology and oncology patients (PASSPORT 2). The Journal of Vascular Access. 2020;22(4):568-574. doi:10.1177/1129729820950997
- Urokinase. NICE British National Formulary (BNF). https://bnf.nice.org.uk/drugs/urokinase/
- UK Kidney Association. 2023. UK Kidney Association Clinical Practice Guidelines, Vascular Access for Haemodialysis. https://www.ukkidney.org/sites/default/files/FINAL%20FORMATTED%20Vascular%20access%20for%20haemodialysis%20April%202023.pdf